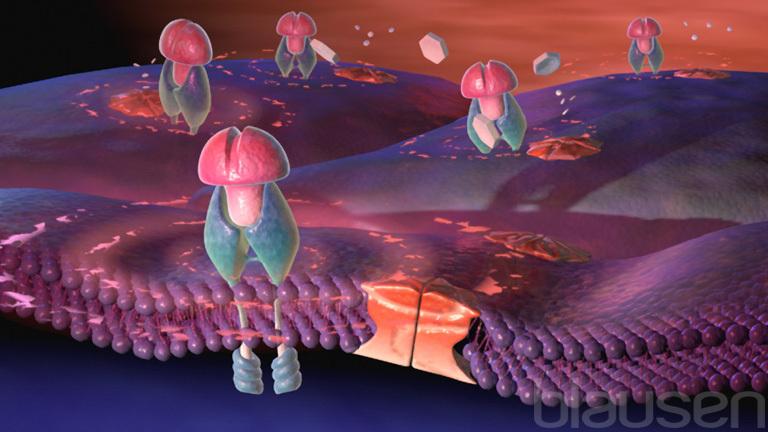
Diabetes Mellitus
During the digestive process, much of the food that is eaten is converted into glucose, commonly known as blood sugar. Glucose circulates in the bloodstream and is used as food for the body's cells. But the cells cannot absorb glucose alone. A hormone called insulin, which is produced in the pancreas, must first bind to the cell surface. When this occurs, cells of the body are activated and are able to absorb the glucose. This process returns the body's blood sugar to a normal level.
Diabetes mellitus is a disorder that affects the body's ability to efficiently utilize blood glucose. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, so glucose cannot be absorbed to refuel the cells. In type 2 diabetes, insulin is produced, but it does not work properly and the glucose is not absorbed consistently by the cells. Both types of diabetes have the same results: glucose is not absorbed by the cells. That is why people with diabetes have high blood sugar levels. Without proper absorption of glucose from the bloodstream, the cells are starving for food. Regardless of which type of diabetes a person may have, people with diabetes must monitor their blood sugar levels. Depending on the type and severity of the disease, diabetes can be managed with diet or with medication.