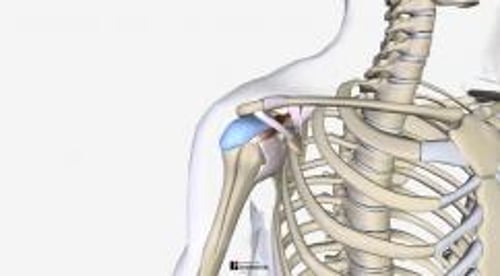
Bursitis is painful inflammation of a bursa (a flat, fluid-filled sac that provides cushioning where skin, muscles, tendons, and ligaments rub over bones).
Movement is usually painful, and bursae near the skin may become swollen and tender.
Pain around bursae suggests the diagnosis, but sometimes analysis of fluid removed from a bursa or imaging tests are needed.
Rest followed by physical therapy, splinting, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes corticosteroid injections usually relieve symptoms.
A bursa normally contains a small amount of fluid, which provides cushioning. Bursae reduce friction and prevent the wear and tear that can occur when one structure rubs over the other. Some bursae are located just beneath the skin (superficial bursae). Others are located under muscles and tendons (deep bursae). If injured or overused, a bursa may become inflamed, and extra fluid may collect in it.
Bursitis is usually caused by
Irritation from unusual use or overuse
It may also be caused by injury, gout, pseudogout, rheumatoid arthritis, or certain infections, especially those caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Often, the cause of bursitis is unknown.
The shoulder is most susceptible to bursitis, but bursae in the elbows, hips (trochanteric bursitis), pelvis, knees, toes, and heels (Achilles tendon bursitis) are commonly affected. People with bursitis of the shoulder usually also have inflammation of tendons around the shoulder (rotator cuff tendinitis—the tendons and other structures that move, rotate, and hold the shoulder in place are called the rotator cuff).
Symptoms of Bursitis
Bursitis usually causes pain and tends to limit movement, but the specific symptoms depend on the location of the inflamed bursa. For example, when a bursa in the shoulder becomes inflamed, raising the arm out from the side of the body (as when putting on a jacket) is painful and difficult. However, bursitis in the elbow may cause swelling but little or no discomfort or limited movement.
SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Acute bursitis develops over hours or days. The inflamed area is usually painful when moved or touched. The skin over bursae located near the surface, such as those near the knee and elbow, may appear red and swollen. Acute bursitis that is caused by an infection or gout may be particularly painful, and the affected area may be red and warm.
SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Chronic bursitis may result from repeated or persistent bouts of acute bursitis or repeated injuries. Sometimes the walls of the bursa become thick. If damaged bursae are subjected to unusual exercise or strain, inflammation tends to worsen. Long-standing pain and swelling can limit movement, making muscles weak. Flare-ups of chronic bursitis may last several months and may return frequently.
Diagnosis of Bursitis
A doctor's evaluation
Sometimes examination of bursa fluid
Sometimes imaging tests
A doctor suspects bursitis if the area around a superficial bursa is sore when touched or when certain joint movements that move or put pressure on deep bursae are painful.
If a superficial bursa, particularly at the knee or elbow, is noticeably swollen, a doctor may remove a sample of fluid from the bursa with a needle. The sample is tested for causes of the inflammation, such as an infection or gout.
X-rays are usually done if bursitis does not get better with treatment or keeps coming back, or if the doctor suspects a problem in an underlying joint such as arthritis.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasonography may be used to help confirm bursitis in a deep bursa.
Treatment of Bursitis
Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medications, and rest
Treatment of any gout or infection
Sometimes injections of corticosteroids
Acute bursitis, if not caused by an infection, is usually treated with the following:
Temporary rest and immobilization (such as with a splint) of the affected joint
Ice applied to the painful area
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Physical therapy after rest and immobilization
Occasionally, stronger pain relievers are needed. Often a doctor may inject a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid directly into the bursa, particularly if the shoulder is affected. This treatment frequently provides relief a few days after the injection. The injection may have to be repeated after a few months. Removing the fluid with a needle also may help reduce pain.
People who have severe acute bursitis are occasionally given a corticosteroid, such as prednisone, by mouth for a few days. As the pain subsides, people can do specific exercises to increase the joint’s range of motion.People who have severe acute bursitis are occasionally given a corticosteroid, such as prednisone, by mouth for a few days. As the pain subsides, people can do specific exercises to increase the joint’s range of motion.
Chronic bursitis, if not caused by an infection, is treated in a similar way, although rest and immobilization are less likely to help. Rarely, surgery is done to remove the bursa.
Often, physical therapy can help restore function. Exercises can help strengthen weakened muscles and reestablish the joint’s full range of motion.
Infected bursae must be drained, and appropriate antibiotics, often against Staphylococcus aureus, are given.
Bursitis often recurs if the cause, such as gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or chronic overuse, is not treated or corrected.
Drugs Mentioned In This Article