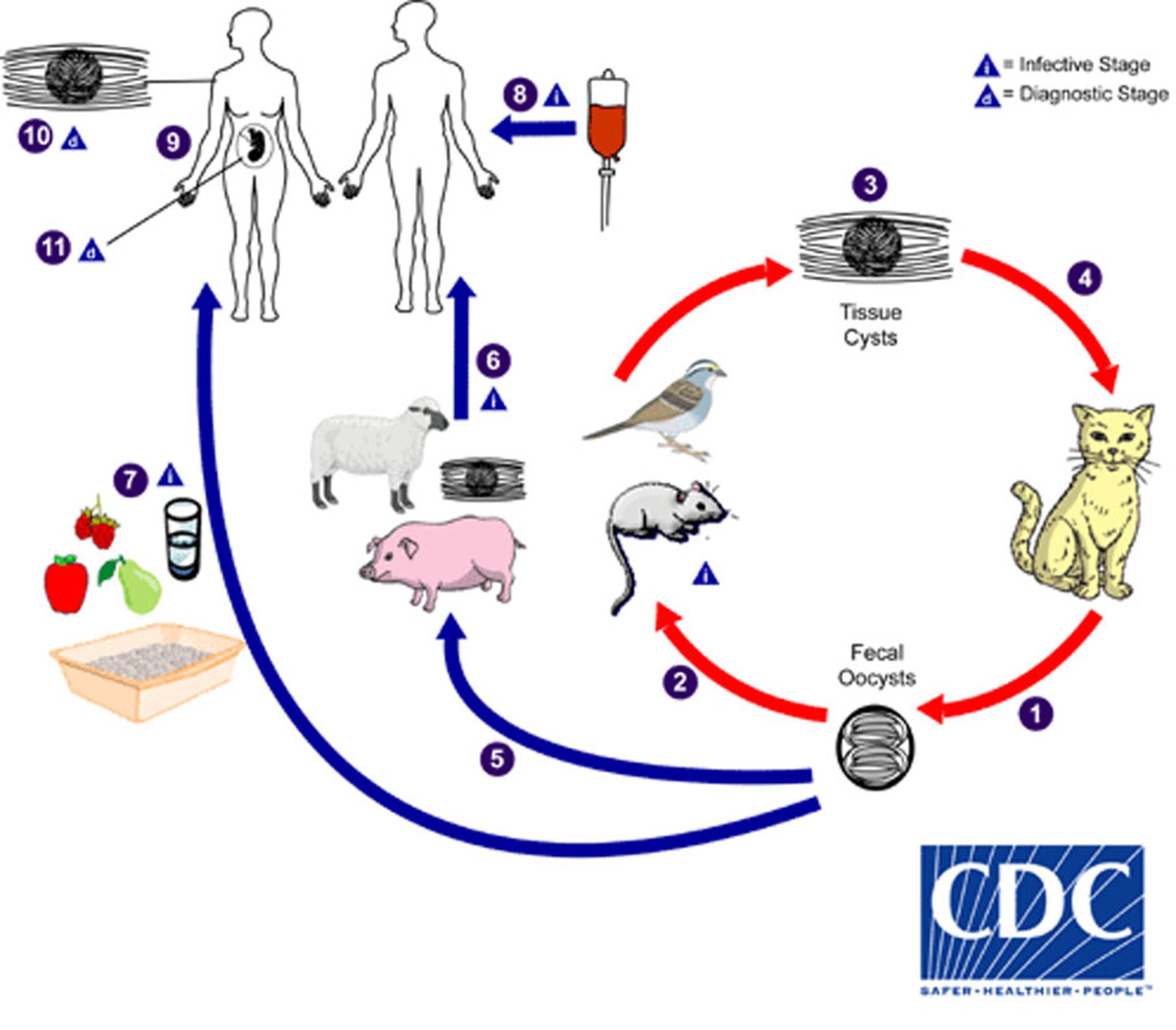
Life Cycle of Toxoplasma gondii
1. Toxoplasma eggs are passed in cat stool. Many eggs are passed but usually for only 1 to 2 weeks. After 1 to 5 days in the environment, eggs become able to cause infection.
2. Other animals (such as wild birds, rodents, deer, pigs, and sheep) may consume the eggs in contaminated soil, water, plant material, or cat litter and become infected.
3. Shortly after the eggs are consumed, the eggs release forms of the parasite that can move (called tachyzoites). Tachyzoites spread throughout the animal's body and form cysts in nerve, eye, and muscle tissue.
4. Cats become infected after eating animals that contain these cysts or after eating the cysts directly.
5. Animals bred for human consumption and wild game may also become infected with cysts after eating cysts in the environment.
6. People can become infected by eating undercooked meat containing these cysts.
7. People can also become infected if they consume food, water, or other materials (such as soil) contaminated with cat stool or when they touch a pet cat's litter and then touch their mouth.
8. Rarely, people can be infected when they have a blood transfusion or organ transplant that contains the parasite.
9. Rarely, the infection can be spread from mother to fetus.
10. In people, parasites form cysts in tissues, usually in muscle and in the heart, brain, and eyes. The cysts may remain for the rest of the person's life without causing symptoms. They may become active and cause symptoms if the person's immune system is weakened by a disorder or medication.
11. Congenital toxoplasmosis can be diagnosed made by testing the amniotic fluid for the parasite's genetic material (DNA).
Image from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Global Health, Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria.